Staying Compliant
The Walker team is committed to helping service professionals stay on the leading edge of emissions control diagnosis and repair for commercial vehicles. Check out this handy reference to EPA standards and what manufacturers are doing to keep heavy-duty vehicles in compliance.
EPA Standards
2007 Highway Rule
Finalized in January 2001 and implemented with the 2007 model year, this controlling regulation’s objective is to reduce harmful pollution from heavy-duty highway vehicles by more than 90%.
2010 EPA Standards
2010 EPA standards require that NOx exhaust emissions (which contribute to acid rain, smog and greenhouse gas levels) be further reduced to 0.2g / bhp-hr, an 83% reduction from 2007 levels.
Note: Environment Canada emissions regulations are aligned with EPA standards.
Manufacturers’ Compliance Efforts
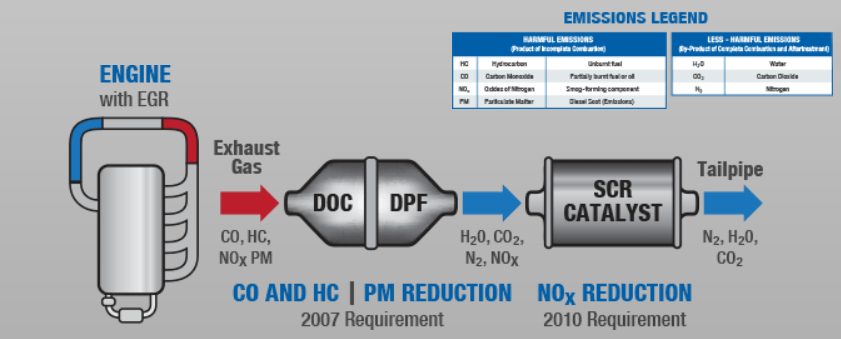
Commercial vehicle manufacturers continue to develop more effective emissions controls for diesel vehicles to meet the required reductions in emissions levels. Within the exhaust system, today’s diesel vehicles utilize "aftertreatment" (post-combustion) technologies to break down or capture harmful emissions.
Aftertreatment Technologies
| Aftertreatment technologies | |
|---|---|
| DOC | DOC – Diesel Oxidation Catalyst A DOC is a device designed to help reduce the amount of exhaust gas pollutants. Modern DOCs for 2007 and later applications have a unique catalyst formulation designed to oxidize harmful emissions (HC and CO) into less-harmful emissions (H2O and CO2). |
| DPF | DPF – Diesel Particulate Filter A DPF, also referred to as a "soot trap," is a device designed to collect harmful particulate emissions produced by diesel engines. Maintenance and service of a DPF is required on most commercial vehicles. In most DPF emissions systems, the filters are designed to be accessed for cleaning by separating the filter assembly from the exhaust system. It is essential to inspect and replace all worn or damaged exhaust components - in front of and behind the assembly - when cleaning the DPF. |
| SCR | SCR – Selective Catalytic Reduction Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is a process of removing nitrous oxides (NOx) through a chemical reaction where diesel emissions are converted to nitrogen and water. |
| EGR | EGR - Exhaust Gas Recirculation EGR systems direct exhaust gases into the engine intake where nitrous oxides (NOx) emissions are reduced. |
Learn more about quality commercial vehicle exhaust parts, find the right heavy duty part, or find a local repair shop today.
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be used in lieu of seeking professional advice from a certified technician or mechanic. We encourage you to consult with a certified technician or mechanic if you have specific questions or concerns relating to any of the topics covered herein. Under no circumstances will we be liable for any loss or damage caused by your reliance on any content.